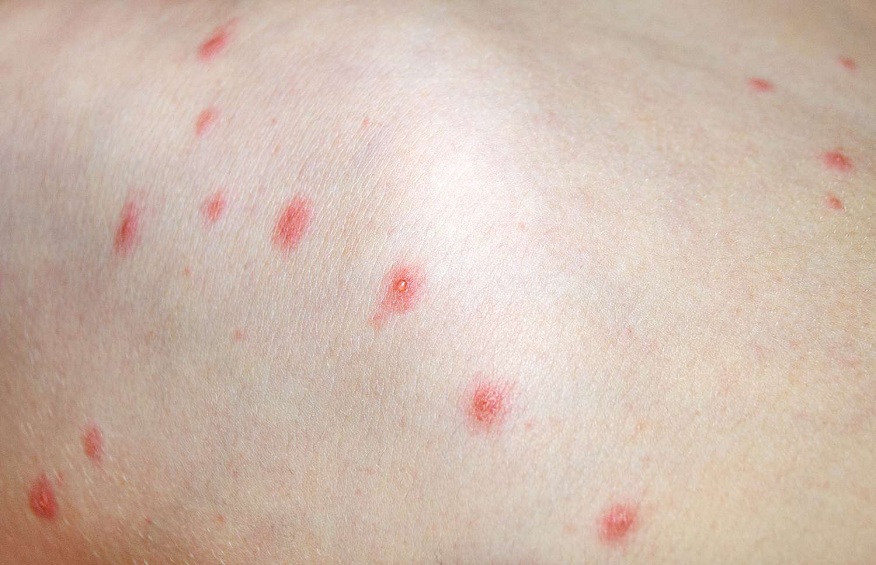
Varicella (or chickenpox), caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), is a highly contagious viral infection that primarily affects children but can also strike adults. While it often resolves on its own without severe complications, understanding the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of varicella is crucial for managing the illness effectively.
What are Its Complications?
Complications from varicella are rare but can be serious, especially in specific populations. Pregnant women, newborns, infants up to four weeks old, and individuals with weakened immune systems face a higher risk of complications. These complications may include:
- Bacterial skin infections
- Pneumonia leading to breathing difficulties
- Encephalitis (inflammation of the brain)
- Reye’s syndrome (swelling of the liver and brain)
- Bleeding disorders
- Sepsis (severe immunological reaction to infection, leading to systemic inflammation and organ dysfunction)
It’s essential to seek medical attention if any of these complications arise during or after a varicella infection.
How Can It Be Diagnosed?
Diagnosing varicella Zoster is often simple for healthcare professionals. The distinctive rash and a brief discussion about symptoms are usually sufficient. However, for those unsure of their chickenpox history, a laboratory test can confirm the presence of the virus. This is especially crucial if exposure to someone with chickenpox occurs, helping individuals understand their susceptibility to the disease.
Knowing the difference between chickenpox and shingles is essential, as the latter can occur later in life when the virus reactivates. Shingles symptoms include an intensely painful rash along a nerve path, accompanied by fever, headache, and other systemic symptoms. Postherpetic neuralgia, a lingering pain after the blisters subside, is also a potential complication of shingles.
How to Treat It?
While there is no cure for varicella, the infection typically resolves within a week or two without specific treatment. However, certain measures can alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
- Pain-relieving drugs like acetaminophen may help manage fever and discomfort. However, avoid aspirin-containing products.
- Hydration is crucial to prevent dehydration.
- Consuming sugar-free popsicles can ease mouth soreness.
- Itching, a common symptom, can be minimized with topical ointments, cool baths, and oral antihistamines.
- Antiviral medications like acyclovir may be prescribed in specific cases, such as during pregnancy, for adults with early diagnoses, newborns, and individuals with weakened immune systems. These medications reduce symptom severity but do not cure the disease.
How Can It Be Prevented?
Preventing varicella is possible through vaccination. The varicella vaccine is about 90% effective and recommended for children and adults. Two types of VZV vaccines are available, including:
- Varivax – A standalone chickenpox vaccine for individuals aged 12 months and older
- ProQuad – A combination vaccine that includes vaccines for measles, mumps, and rubella (MMRV)
Both vaccines are administered on specific schedules and effectively protect against varicella and its potential complications.
Additionally, practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, isolating household members with chickenpox, and disinfecting surfaces touched by infected individuals can help prevent the spread of the virus.
Take Away
Understanding varicella is vital for quick diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and effective prevention through vaccination. By being aware of the complications, recognizing symptoms, and following preventive measures, individuals can minimize the impact of this contagious and sometimes serious viral infection.







